Batrachospermum Occurrence:- (1) Batrachospermum is fresh water alga. (2) It is found in clear, cool, and running streams. (3) Deepwater plants are dark violet or reddish in color. But the shallow-water species are olive green. (4) The intensity of light changes the color of pigments. (5) The thallus is attached to the substratum. Vegetative structure (1) The thallus of an adult plant is soft, thick, filamentous. (2) It is freely branched and gelatinous. (3) The central axis is made up of a single row of large cells. Whorls of branches of limited growth are developed on this axis. (4) These branches are filamentous and dichotomously arranged. (5) The main axis is corticated. It consists of a row of elongated cylindrical cells....
Cycas
Distribution of Cycas:-
It is the sole genus of the family Cycadaceae, that is delineated in the Asian nation. it's
got regarding fifteen species (Sporne, 1965), twenty species (Willis, 1966)
that area unit cosmopolitan in japan also as occident from Madagascar, jap the coast of the continent to Japan and Australia touching China and the Asian nation.
 |
| Cycas Revoluta |
In our country a number of the species-area the unit found growing profusely within the South Andaman and Nicobar islands, Madras, Mysore, Malabar and in North East in the geographical area, Assam, Kingdom of Nepal and geographic area. a number of of the species also are found in Asian nation and Ceylon.
 |
| Male Cone -Cycas |
Morphology
or External Feature of gymnosperm genus:-
Cycas Plant
could be a well-developed tree. It grows in xerophytic condition and is slow-growing plant reaching a height of 3-5 meters in regarding one hundred years
.It has true root, stem, and Leaves.
Root:-
It has Tap
root system. The root area unit well developed, branched, and fix into the
soil. Some branches of the secondary root are apogeotropic in order that they come
out from the soil.
They become
related to Blue chlorophytes like blue-green algae and Anabaena .they are
continual branched like corals thus referred to as Corraloid roots.
Stem:-
The Stem is
stout and stay underground for several years . When arial ,it is branchless and
armoured with thick persistant leaf bases .leaf happens as a crown within the
higher half .
Female half contain 3 kinds of leaves : Scaly leaves,Foliage
leaves and sporophyll kind Leaves.
Bulbils is
seen within the lower a part of Stem in cycas revolute.
Leaves :-
Leaves area
unit polymorphism kind
The foliage
leaves and scaly leaves .
Foliage
leaves area unit pinnately compound and having 500-100 leaflets organized
within the rachis .The leaflets area unit sessile and have single unbranced
vein .
The leaflet is harden .Scaly leaves
organized alternate wit hfoliage leaves .They are brown ,hard persistant and
non-photosynthetic.
Secondary Growth:
The mature
traditional root shows secondary growth on each the lateral sides of primary
vascular tissue. aspect|in conjunction with|beside|at the side of|together
with} the inner side of primary bast develops the cambium. It cuts off
secondary bast on outer facet and secondary vascular tissue on the inner facet.
when someday the cells of the pericycle opposite to the protoxylem strands
conjointly become meristematic and behave as cambium, cutting bast on the outer
facet and vascular tissue on the inner facet.
Thus, an
entire ring of cambium is created that forms an entire ring of secondary
vascular tissue on the inner facet and complete ring of secondary bast on the
outer facet. the first bast is crushed within the due course of development and
seems within the type of crushed layer higher than the secondary bast.
Simultaneously
the formation of periderm conjointly starts. The cells of the outmost layer of
the cortex become meristematic (also referred to as cork cambium) and begin
cutting cork cells on the outer facet and secondary cortex on the inner facet.
within the course of the formation of cork, the cells of the epiblema area unit
crushed
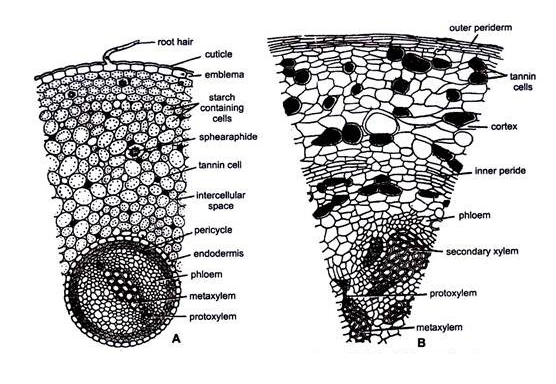
Internal Sructure of Root :-
Normal root:
Epiblema:
It is the
outmost limiting layer and consists of single layer of skinny walled cells. a
number of its cells create to root hairs.
Cortex:
Epiblema
surrounds the multilayered zone of skinny walled parenchymatous cortex with
various living thing areas. The cells of the cortex area unit stuffed with
starch. Some tannic acid cells, mucilage cells and generally sphaeraphides
(calcium salt crystals) also are gift within the cortex. The innermost layer of
the cortex forms the endodermis that is characterized by the presence of
casparian strips.
 |
| Normal Root -Cycas |
Vascular tissue:
Endordermis
is followed by multilayered parenchymatous pericycle. tube bundles area unit
radial. vascular tissue is diarch and exarch i. e., protoxylem is towards the
periphery). The protoxylem consists of spiral tracheids whereas the metaxylem
consists of scalariform thickenings. Vessels area unit absent. Alternating with
the protoxylem teams area unit gift bast cells consisting of sieve tubes and
bast parenchyma. The companion cells area unit fully absent.
Coralloid Root:
Epidermis:
In young
root, it's like traditional root. However, in previous root the outmost tissue
is periderm. It consists of two to five layers of dead cells.
b. Cortex:
The cortex
is wider compared with the traditional root. A green protoctist zone is gift
nearly within the middle of the cortex and divides it into outer cortex and
inner cortex (Fig. 9A, B).
The
protoctist zone consists of loosely connected, radially elongated skinny walled
cells occupied by blue chlorophyte (Anabaena cycadae, blue-green algae punctiforme,
Oscillatoria), microorganism (Azotobacter, bacteria genus radicicola) and a few
fungi. the most perform of those roots is organic process because of the
presence of cyanophycean members. Endodermis is comparable to traditional root
 |
| Corlloid Root -Cycas |
Vascular tissue:
Endodermis
is followed by multilayered parenchymatous pericycle. tube bundles area unit
radial. vascular tissue is triarch and exarch.
Secondary
growth is incredibly rare or absent. No secondary vascular tissue or secondary
bast area unit developed though cork and cork cambium area unit gift.
Stem:
Epidermis:
It is the
outmost layer of the stem. it's created of succinctly organized thick walled
cells. cuticle is burst because of the armour of persistent leaf bases .
Cortex:
Epidermis
encloses the cortex. It forms the main portion of the stem. it's composed of
parenchymatous cells that area unit stuffed with sizable amount of starch
grains. These starch grains area unit the supply of amylum starch. Therefore,
C. revoluta is popularly referred to as amylum palm.
 |
| Cycas Stem |
Scattered
within the cortex area unit varied mucilage canals. every mucilage canal is
lined by several radially elongated animal tissue or body fluid cells .which
secrete mucilage. These canals area unit connected with those of the pith with
the assistance of the medullary rays. The innermost layer of cortex is
endodermis. it's not distinct.
Vascular Bundle :
The tube
cylinder is enclosed by not terribly conspicuous pericycle. Like angiosperm
stems tube cylinder consists of the many conjoined, collateral, open, endarch
tube bundles organized in a very ring (ectophloic slphonostele). The vascular
tissue consists of tracheids and vascular tissue parenchyma .
Vessels area
unit absent. Outside the vascular tissue is that the bast that consists of
sieve tubes and bast paraenchyma. Companion cells area unit absent. The
vascular tissue is separated from the bast with the assistance of primary
combium. The cells of the first cambium area unit brick formed.
The cells
lying in between the tube bundles type the medullary rays. These area unit
parenchymatous and connect the pith with the cortex. every vascular tissue is
one celled wide and one to twenty cells long.
Pith:
In the
centre of the stem is gift giant canals leaf traces large pith consisting of
parenchymatous cells that area unit made in starch (sago starch). an outsized
variety of mucilage canals also are gift, that area unit specifically similar
in structure with the mucilage canals gift within the cortex.
Rachis:
Epidermis:
It is the
outmost covering. it's created of succinctly organized thick walled cells. it's
single bedded, coated with thick cuticle and has stomata.
Hypodermis:
Epidermis is
followed by layer. it's differentiated into outer 2-3- layers of parenchyma
(Chlorophyll containing skinny walled cells) and inner 4-6 layers of
sclerenchyma (thick walled, hard cells.
 |
| Rachis in Cycas |
Ground tissue:
Below the
sclerenchyma is gift an outsized tissue created of skinny walled parenchymatous
cells. it's referred to as ground tissue. during this region area unit gift
several sticky canals and tube bundles.
Vascular bundles:
Vascular
bundles area unit organized within the form of inverted Greek letter ‘omega’
.Each fibrovascular bundle is conjoined, collateral, endarch, open and
diploxylic i. e., consists of centripetal and centrifugal vascular tissue and
is enclosed by bundle sheath.
Xylem is
gift towards the inner facet and consists of tracheids and vascular tissue
parenchyma. Vessels area unit absent. bast is gift towards the outer facet of
the fibrovascular bundle. It consists of sieve tubes and bast parenchyma.
Companion cells area unit absent, Cambium is gift in between the vascular
tissue and bast.
Leaflet:-
Epidermis:
It is the
outer most single layer created of square cells. The higher cuticle is complete
whereas the lower cuticle is interrupted by many sunken stomata gift within the
region of the wings. The higher and lower cuticle is roofed by a thick layer of
culicle.
 |
| Leaflet internal |
b. Hypodermis:
Below the
cuticle happens the thick walled sclerenchymatous layer. it's single bedded
within the region of blade however within the region of middle rib it becomes
2-3 bedded thick. 2 to 5 layers of sclerenchymatous cells also are gift higher
than the lower cuticle solely within the region of the middle rib. It helps in
checking the speed of transpiration and protects the tissue from excessive
heat.
c. Mesophyll:
A well-developed
mesophyll tissue is gift within the leaflet. it's differentiated into palisade
tissue and spongy parenchyma. Palisade tissue is gift within the type of
continuous layer below the sclerenchymatous layer. Spongy parenchyma gift
solely within the wings directly higher than the lower cuticle. it's created of
loosely organized oval cells stuffed with plastid. These cells have several
living thing areas stuffed with air.
Vascular bundle:
A single
giant fibrovascular bundle is gift within the middle rib region of the leaflet.
it's enclosed by one layer of sclerenchymatous cells, referred to as bundle
sheath. The fibrovascular bundle is conjoined, collateral, open and diploxylic.
vascular tissue is gift towards the dorsal surface and bast is gift towards the
ventral surface.
Xylem and
bast area unit separated by a non-functional strip of cambium. Centrifugal
vascular tissue is delineate by 2 little teams on either facet of the
protoxylem. The remaining area of the fibrovascular bundle is stuffed with
skinny walled parenchymatous cells.
Structure of microsporophyll:
Each
sporophyl represents a reproductive structure. it's a planate, woody and
triangular structure. it's differentiated into higher or distal, sterile region
referred to as apophysis and proximal wedge formed fertile half. every
sporophyl bears many hundred microsporangia (pollen sacs) on its dorsal surface
(more than 1000).
 |
| Male Cone |
Microsporangia
area unit organized in clusters of three to six. every cluster or cluster of
microsporangia is named sorus. In between the microsporangia covering hairs
area unit gift that facilitate within the dispersion of the microspores and
defend young sporangia.
Female procreative Organs:
Female
procreative organs area unit megasporophylls. every feminine plant per annum
produces various megasporophylls in acropetal succession higher than every
crown of foliage and scaly leaves. there's no feminine cone formation. the
quantity of the megasporophylls is way quite the quantity of the foliage leaves
on the stem.
During the
formation of the megasporophylls the top plant tissue isn't ran down like that
of male cone and thus, the expansion of the stem continues, and therefore in
feminine plant growth is monopodial.
Structure of Megasporophyll:
Each
sporophyll (carpel) is thought to be a changed leaf. it's regarding twelve.7 cm
to 25.4 cm long and might be divided into three parts: higher ivied portion,
middle ovule bearing portion and lower stalk. Ovules area unit fashioned on the
lateral facet of the center portion. The higher portion is pinnated and every
pinna is tapering to some extent.
 |
| Structure of Megasporophyll |
Two lateral
rows of ovules area unit gift on the lateral facet of the center portion.
In
{cycas|Cycas|genus gymnosperm genus|gymnosperm genus} there's a good variation
concerning the pinnated character of sporophyll and also the variety of ovules
per foliage as a result of that in varied species of Cycas gradual reduction
in megasporophylls will be derived.
The
megasporophylls of C. revolula area unit pinnated whereas those of C.
circinalis C. rumphii and C. beddomei area unit ovate pointed structures. In C.
pectinata and C. siamensis they're orbicular or parallelogram structures .
The bedded
portion is well developed in C. revoluta, C.pectinata and C. siamensis however
reduced in C. circinalis, C. beddomei and C. rumphii .The margin of plate is
serrate or rough in C.circinalis, C.beddomei and C. rumphii. the quantity of
ovules take issue in several species of gymnosperm genus. It is 1-6. pairs in
C.revoluta, C. Circinalis and just one try in C. norambyana. Megasporophylls
area unit coated by yellow or brown hairs.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks