Batrachospermum Occurrence:- (1) Batrachospermum is fresh water alga. (2) It is found in clear, cool, and running streams. (3) Deepwater plants are dark violet or reddish in color. But the shallow-water species are olive green. (4) The intensity of light changes the color of pigments. (5) The thallus is attached to the substratum. Vegetative structure (1) The thallus of an adult plant is soft, thick, filamentous. (2) It is freely branched and gelatinous. (3) The central axis is made up of a single row of large cells. Whorls of branches of limited growth are developed on this axis. (4) These branches are filamentous and dichotomously arranged. (5) The main axis is corticated. It consists of a row of elongated cylindrical cells....
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction |something new
- Kingdom- Plantae
- Division- Gymnospermophyta
- Order –Epheriadales
- Family –Epherideacae
- Genus - Ephedra
Ephedra is that the solely genus in {family
ephedraceae|Ephedraceae|family |gymnosperm family} and order Ephedrales. it's diagrammatical
by fifty species.
 |
| Ephedra |
8 Species is Found in Republic of India that is distributed
within the region of Haryana,Punjab,Rajasthan and a few a part of Kasmir.
Morphological options of Ephedra:
The plant body is sporophytic and shows xeric characters.
 |
| Ephedra Morphology |
principally the plants area unit woody shrubs and its wood kind is
picnoxylic ( means that show hardness
and economical necessary )a only a few species area unit lianas(Cimbing on
different tree ) and a few species grow into atiny low tree. E. compacta
reaches thirty cm tall E. triandra could be a tree.
Root:-
In this genus of Gymnosperms it's no protoctist zone or
mycorrhiza. there's a outstanding underground faucet system. soon the
accidental roots develop.
Stem:-
It shows Equistem like
look and its stem is additionally feels like stem of eqiustem .
It shows
Phylloclode kind modification means that Stem show chemical change .
The
Branches is additionally inexperienced at node and segment .
The branching
starts early at the cotyledonary stage.
The top plant tissue has well marked
membrane layer however the expansion of segment is freelance because of the
presence of the meristemetic zone at its base.
This zone dries up at the top of
every season. It leads to the breakableness and shedding of the branches
Leaves:
Leaves area unit snall scaly gift at the node position and
also the variety of leaves rely upon the amount of Ridges and grooves as same
in equistem .
every leaf contains 2 branchless, parallel veins. they're thus
minute that they're of no use i. e., unable to perform chemical change.
The
perform of chemical change is carried by inexperienced stem. within the angle
of every leaf is gift a bud for the branch. True foliage leaves area unit
absent.
Internal Structures of Ephedra:
Stem at node Region Internal Structure :-
 |
| T.S. of Stem |
Epidermis :-
it's the outmost layer
of thick walled cells, lined with a thick layer of cuticle.
Sunken stomata area
unit gift on the slopes of the ridges within the circular pits.
The kind of stomata
is sunken type because of xeric character of genus ,so rate of transpiration is
decrease in sunken stomata.
Hypodermis:-
it's gift just under
the ridges. it's created of sclerenchymatous cells and provides mechanical
strength to the plant and hardness of wood
Beacause in contain polymer covering
over their surface.
Cortex :-
In is
gift between the thick walled sclerenchyma and vascular cylinder. It are often differentiated into
outer and inner cortex.
The outer cortex contains 2-3 layers of radially
elongated palisade tissue and inner cortex consists of 2-3 layers of spongy
parenchyma.
The cells of outer and inner cortex area unit loosely organized
with giant animate thing areas and area unit given chlorophyl to perform the
perform of chemical change.
a couple of patches of scleranchymatous cells might
also occur within the cortex to supply mechanical support to the young axis.
Endodermis :-
it's the innermost
layer of cortex. it's not simply distinguishable from the plant tissue cells.
Pericycle :
It is gift below the endodermis. it's single stratified and sick outlined.
Vas
it's endarch,
siphonostele and consists of the many vascular
bundles organized in a very ring. vascular bundles area unit conjointed, collateral,
open and endarch.
the amount of primary vascular strands is mostly eight, out of that four
tiny represent the foliar traces whereas the opposite giant four area unit stem
bundles.
Foliar traces run upto the node. vascular tissue consists of
tracheids, vessels and vascular tissue parenchyma.
because of the presence of
the vessels the shrub resembles angiosperms. The bast consists of sieve cells,
bast parenchyma and simple protein cells.
bast and vascular tissue area unit
separated by a slender strip of cambium.
Medullary Ray :-
Broad, parenchymatous medullary rays area unit gift in
between the vascular bundles. Medullary
rays connect the pith with cortex.
It is gift within the centre. it's created up off skinny
walled parenchymatous cells.
close to the node its cells become powerfully
woody forming a peridermal diaphragm that accounts for the fast separation of
the branches within the region
Secondary Growth :-
The secondary growth takes place by the activity of
intrafascicular cambium and interfascicular cambium.
 |
| Mature Stem |
once forming an entire
ring of cambium, the vascular tissue cells cut of secondary bast on the outer
facet and secondary vascular tissue towards the inner facet.
Due to formation of the secondary tissues, primary bast is
crushed and also the primary vascular tissue is pushed towards the inner facet
at the bottom of the secondary vascular tissue.
additionally to plant tissue
cambium additionally forms medullary rays (secondary). These rays area unit
long, broad (multiseriate) and traverse between secondary vascular tissue and
secondary bast.
Radial Longitudinal Section :-
xylem tracheids, vessels and medullary rays area unit clearly
visible.
Medullary rays area unit cut lengthwise and their length and height
area unit unconcealed .
every vascular ray consists of on an irregular basis
distributed ray cells and ray tracheids. Tracheids possess seagirt pits on
their radial and tangential walls.
In vessels, the seagirt pits are organized
within the same method as tracheids.
Tangantial Longitudinal Section :-
Like R.L.S. in T.L.S. also, the xylem, tracheids, vessels and
medullary rays area unit clearly visible however they're cut transversally
here.
(Bordered pits and straightforward pits area unit seen on the radial and
tangential walls.
The medullary rays area unit elongated and on their
tangential walls area unit gift easy pits.
Leaf:
The transversal section of scaly leaf is oval in form and may
be differentiated into cuticle, mesophyll tissue and plant tissue.
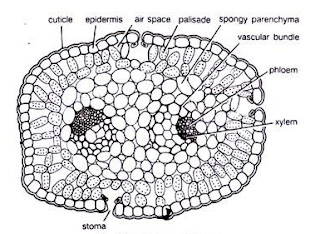 |
| T.S. of Leaf |
Epidermis :-
It is outer most single layer of thick walled elongated
cells.
The cells area unit lined with thick cuticle. Sunken stomata area unit
gift .
Mesophyll tissue:
Two or 3 layers of palisade tissue area unit gift inner to
cuticle.
The cells area unit crammed with plastid and huge animate thing areas
area unit gift between them.
within the centre of the leaf parenchymatous
tissue is gift.
Vascular tissue:
Two vascular bundles
area unit embedded within the parenchymatous tissue. The vascular bundles area unit collateral and closed.
vascular tissue is gift towards the side.
Root:
The transversal section of root shows single layer epiblema,
outer cortex (composed of collenchymatous cells), inner cortex (composed of
parenchymatous cells) endodermis and pericycle.
vascular bundles area unit radial and exarch. the
basis could also be diarch or triarch.
Reproduction in Ephedra:
Ephedra is monogenesis (produces 2 kinds of spores:
microspores and macrospores) and dioecian (both these kinds of spores area unit
made on 2 totally different plants of identical species.
E. fuliata is
autoicous. Microspores area unit shaped in male flowers whereas megaspores area
unit shaped in feminine flowers.
These flowers area unit gift within the variety of cone like
compound strobili.
Male flowers area unit gift within the variety of male
reproductive structure whereas feminine flowers area unit gift within the
variety of female reproductive structure.
each male and feminine strobili
area unit compound i. e.,the cone axis bears pairs of bracts that be either
microsproangiate or release shoots.
Male reproductive structure (Staminate Strobilus):
Male strobili arise in clusters from the nodes of the
branches. every reproductive structure is rounded, ovoid or spherical in form
and arises within the axis of a leafage.
 |
| Male Reproductive part |
Their variety at the node depends upon
the amount of scale leaves.
Each reproductive structure incorporates a central axis that
bears 2-12 pairs decussately organized easy, broad and cupped bracts.
Lower
most 1-2 pairs of bracts area unit sterile. within the angle of every fertile
husk arises a male flower or male flower .
A male reproductive structure with
many male flowers are often compared with AN inflorescence.
Male flowers:
Each male flower has 2 bilabiate skinny bractioles (perianth)
that encloses a reproductive structure.
Bracteoles area unit united at the
bottom.
The flower incorporates a short stalk called microsporangiophore and 2,
eight to 12 microsporangia at its tip .
Microsporangia area unit sessile and
erupt terminally. Male flower is additionally known as easy reproductive
structure.
A compound male reproductive structure, therefore, consists of the
many such strobili.
Development of microsporangium:
The development of spore case is eusporangiate.
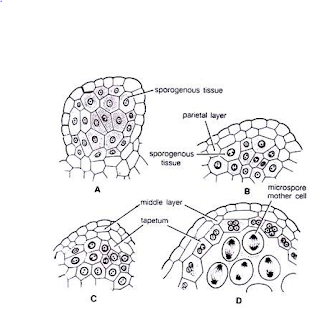 |
| Development in Microspore |
Microspangia arise at the tip of microsporangiophore.
The microsporangiophore arises as tiny protuberance within
the angle of the fertile husk of male reproductive structure.
The apex of microsporangiophore becomes compound once growing
for a few time.
Each lobe represents a spore case.
Few layer cells in every lobe enlarge in size.
These cells consist giant nuclei, denser cytoplasts and area
unit called cell cells.
These cells divide periclinally into outer primary wall cells
or primary membrane bone cells and first reproductive structure cells .
Primary reproductive structure cells any divide by 2
periclinal divisions to differentiate middle wall layer, inner tapetal layer
and reproductive structure cells.
The primary wall cells perform directly because the outer
wall of the spore case.
According to some staff, the first wall cells divide
periclinally to create 3 stratified
thick wall.
The reproductive structure cells divide any to create
sizable amount of spore mother cells.
every spore cell divides by meiosis to
create four haploid microspores organized in a very linear foursome.
Structure of spore grain:-
Pollen grain is that the initial cell of the male flora.
every spore grain is elliptical, cell organ and has 2 wall layers.
The outer
wall layer is thick and is named exine whereas the inner male layer is then and
is named intine.
(Ovulate Strobilus) or
female Cone:-
They usually arise in pairs at every node within the angle of
scale leaves.
 |
| Female Cone |
A feminine reproductive structure seems to be AN elliptical
structure with a pointed apex .
It retains identical compound structure because
the male reproductive structure. It consists of a brief axis to that area unit
hooked up 3 or four pairs of decussate bracts.
In E. artefact these bracts area unit swollen and juicy .
All
the trys of bracts area unit sterile except the topmost one that bears a pair
of ovules in its angle and should be multifariously colored.
Out of the pairs
of the ovules only 1 survives and it takes up a false terminal position.
Structure of ovule (megasporangium):
Longitudinal section of AN ovule shows that it consists of a
mass of parenchymatous cells within the centre. it's known as plant structure.
The plant structure is encircled by a two-layered envelope.
These area unit
typically selected as outer and inner integuments.
The outer envelope is made
by four segments and receives four bundles whereas the inner one is made of 2
segments and receives 2 bundles.
The lower half the inner envelope is coalesced to the plant
structure however higher is free and prolongs into a protracted aperture
tube.
By the time of fecundation just under the aperture spore chamber
develops. spore chamber in shrub is that the deepest illustrious among the
Gymnosperms.
the ground of the spore chamber is made by feminine gametophytic
tissue and not by the plant structure as in different gymnosperms.
Development of Ovule:
Development of the ovule takes place within the variety of
a tiny low cellular protuberance.
This protuberance will increase in size and
becomes the plant structure.
shortly neighbour cells of the bottom forms inner
and outer integuments. Inner natural covering surrounds the plant structure
except the highest wherever it type atiny low gap known as aperture.
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
A layer cell cell differentiates within the plant structure.
It divides periclinally into outer membrane bone cell and inner spore cell. The
latter is pushed quite deep into the nucellar tissue.
The spore cell divides meiotically to create four hapliod
megaspores. usually the bottommost spore (towards the chalazal end) remains
purposeful.
It enlarges and provides rise to feminine flora (first cell of the
feminine gametophyte) and also the remaining higher 3 megaspores degenerate.
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction
Conclusion : we have learnt Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction |something new
Conclusion : we have learnt Ephedra-General Characters,Distribution,Thallus and Reproduction |something new
This looks like it will be very informative - many thanks!
ReplyDelete