Batrachospermum Occurrence:- (1) Batrachospermum is fresh water alga. (2) It is found in clear, cool, and running streams. (3) Deepwater plants are dark violet or reddish in color. But the shallow-water species are olive green. (4) The intensity of light changes the color of pigments. (5) The thallus is attached to the substratum. Vegetative structure (1) The thallus of an adult plant is soft, thick, filamentous. (2) It is freely branched and gelatinous. (3) The central axis is made up of a single row of large cells. Whorls of branches of limited growth are developed on this axis. (4) These branches are filamentous and dichotomously arranged. (5) The main axis is corticated. It consists of a row of elongated cylindrical cells....
Poaceae
Diagnostic Features :-
(1) Stem,cylinder,jointed,with generally hollow internodes and intercalary meristems.
(2) Leaves ligulate,simple and forms sheathing around base.
(3) Flowers arranged in spikelets which in turn are grouped in spike or panicles.
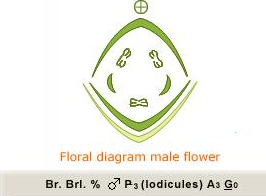
(4) Each flower is sessile,bisexual may be unisexual ,zygomorphic,hypogynous.
(5) Each flower is covered by scales,That is lemma and plea.The lemma has a stiff awn.
(6) Perianth 2-3 called lodicules.
(7) Anthers divaricate and versatile.
(8) Monocarpellary,ovary superior,unilocular.
Distribution and habit:-
It is a family with worldwide distribution.Inindia ,the family is represented by 239 genera and 1180 species.
Root :-
Adeventatious root system,stilt roots are present in sugercane and maize to give extra .support.
Stem :-
Herbaceous,may be modification to rhizome,stolon or runner,jointed and has hollow internodes in maize ,woody in bambusa,supra-nodal intercalary meristem present in many species.In some plants ,many branches of equal length appear from the base of plants.
Leaves :-
Each leaf is composed of two partd,sheath and blade,sheath encircles the culm,sessile,ligulate in bambusa,parllel venation.
Inflorescence:-
Stalked or sessile,spiklets borne on the rachis ,spike of spikelets in wheat ,each spikelets consist of one or more flowers and their subtending bracts are arranged on rachilla or inflorescence axis,at the base of spikelet are present two sterile glumes. In a few types,either the first glume or both the glumes are absent.
Flower :-
Small,usually called florates,bisexual or unisexual,zygomorphic,hypogynous.Each florets consist of two bracts called lemma and palea,lemma or the flowering glume is greenish,keeled and awned ,palea,representing the bracteolate,is thin,membranous and bears a flower in its axil.
Perianth :-
Absent or reduced to 2 or 3 ,minute scales like called lodicules.
Androecium :-
Stemans usually 3,filaments free,anther bithecous,basifixed or versatile,introse,dehiscence longitudnally.
Gynoecium :-
Bicapellary or tricarpellary ,syncarpous,ovary superior,unilocular with one ovule,placenta basal, style two,stigmas feathery
 |
| Poaceae Floral diagram |
Triticum Aestivum
Inflorescence :- Spike of spikelets
Flower :- Sessile,bracteate,bract represented by an multicostate scales called lemma,bracteolate is represented by marginal folded papery scales called palea.
Perianth :- Two lodicules free,anteriorly placed inferior.
Androceium :- Stemans 3 .polyandrous,anther bithecous,fixation versatile,divaricate,longitudnal dehiscence,filament long inferior.
Gynoecium :- Monocarpellary ,unilocular,uniovulated,basal placentation ,hairy ovary,triangular,two feathery stigmas appearing directly from the tip of the ovary.
 |
| Poaceae family floral formula,diagram |
Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks